Overview
- Amazon S3 for website hosting.
- AWS Route53 for DNS and domains.
- AWS Certificate Manager for SSL certificate.
- CloudFront for CDN and TLS termination.
S3
Creating the buckets for website hosting on s3 is well documented on their documentation.
You can create two buckets, www.example.com and example.com and have the www-bucket to redirect requests to non-www version(example.com).
Route53
Create A-Record to point to your s3 buckets(or CloudFront).
AWS Certificate Manager
ACM is Amazon’s certificate manager service. I am using ACM to provision a certificate for my custom domain. Amazon automatically takes care of its renewal and it issues a wildcard certificate for free.
CloudFront
With AWS CloudFront, we can distribute our website assets around the globe. Also, we can enforce the bucket access only through CloudFront, so that users cannot go directly to our buckets.
Few things to point out:
Origin Domain Name: Make sure it’s your s3 bucket URL and don’t select the bucket from the dropdown. E.g.<bucket_name>.<region>.amazonaws.com, not the<domain>.s3.amazonaws.com.Restrict Bucket Access: Setting this to yes will ensure that your users access your files in s3 bucket using only CloudFront URLs.Viewer Protocol Policy: SelectRedirect HTTP to HTTPSforhttp://example.com->https://example.comCompress objects automatically: Select yes if you want CloudFront to automatically compress and serve files of certain types.Default Root Object: the name of the main HTML file. Usually it isindex.html.
Error Page
When you try to go to a non-existent page on your website, cloudfront returns 403 Forbidden error. You can handle this from CloudFront to return error page when your origin returns 403 permission denied error.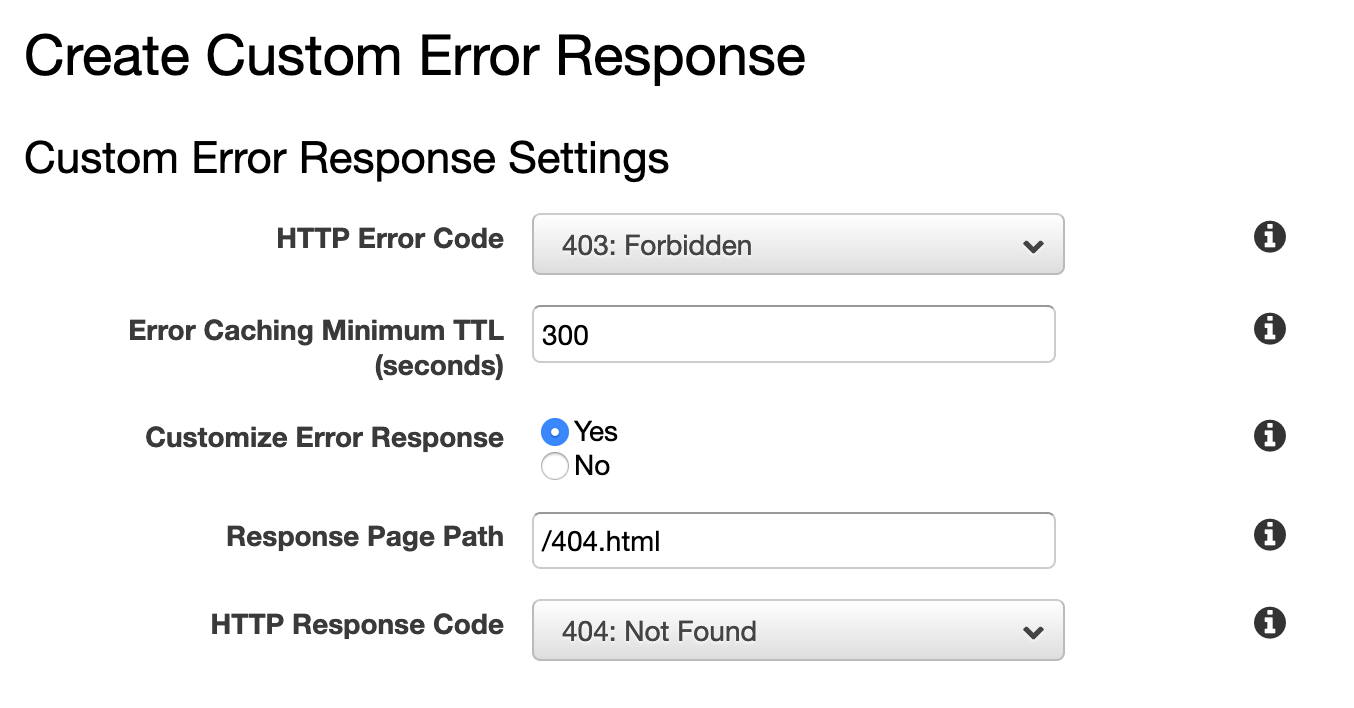
AWS Error Page Configuration